Trrarrusian body (A1-0): Difference between revisions
(→Cells) |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
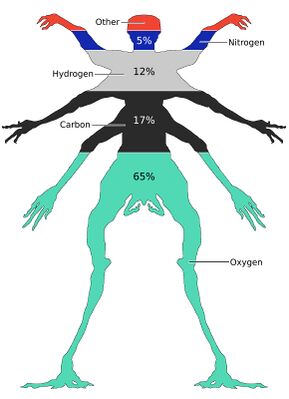
Trrarrusians are a carbon-based specie, composed of various elements, specifically carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen, phosphorus and titanium. These elements are located in both cellular and extracellular mass. | Trrarrusians are a carbon-based specie, composed of various elements, specifically carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen, phosphorus and titanium. These elements are located in both cellular and extracellular mass. | ||
The adult trrarrusian male body is composed of about | The adult trrarrusian male body is composed of about 60% water in total, shared between extracellular fluids, blood plasma, interstitial fluids, and cellular fluids. The pH is carefully maintained rigorously, keeping a slightly alkaline pH level between 7.85 and 7.95 due to the high ammonia content required for metabolic processes. The most important electrolytes in extracellular fluids are potassium and chloride. Meanwhile, inside cells, the main electrolytes are sodium and phosphates. | ||
=== Cells === | === Cells === | ||
| Line 69: | Line 69: | ||
|} | |} | ||
Trrarrusian bodies are composed of cells. At maturity, there are roughly 59-74 trillion cells, an estimate reached with the volume of an adult trrarrusian body, the volume of each type of cell and the proportion of these cells in the body. The body also coexists with commensalist and symbiotic microorganism inside of it and on its skin, which feed on the excretion and dead cells of the individual, and in some cases serve essential roles in the body such as digestion, synthetizing of molecules and processing of atmospheric ammonia. A significant part of the total mass of the body isn't composed of cells, but extracellular tissues and material, as the protein matrix in which cells are housed, or extracellular fluids. Around 37% of the total mass is composed of symbiotic and commensalist organism, or non-cellular mass such as bones, connective tissues and fluids. | Trrarrusian bodies are composed of cells. At maturity, there are roughly 59-74 trillion cells, an estimate reached with the volume of an adult trrarrusian body, the volume of each type of cell and the proportion of these cells in the body. The body also coexists with commensalist and symbiotic microorganism inside of it and on its skin, which feed on the excretion and dead cells of the individual, and in some cases serve essential roles in the body such as digestion, synthetizing of molecules and processing of atmospheric ammonia. A significant part of the total mass of the body isn't composed of cells, but extracellular tissues and material, as the protein matrix in which cells are housed, or extracellular fluids. Around 37%, or 48 kg of the 130 kg of the total mass is composed of symbiotic and commensalist organism, or non-cellular mass such as bones, connective tissues and fluids. | ||
==== Genome ==== | |||
Cells are able to realize functions thanks to DNA. DNA in trrarrusian cells is located in a nucleus in the centre of the cells, in most cases. This DNA is used for the synthetizing of proteins within the cell, that regulate cell behaviour, metabolic processes and form structural components within and outside the cells. Some cells, as blood cells, lack DNA. | |||
=== Tissues === | |||
The body is composed of multiple different kinds of cells that serve different purposes, the combination of various cells that serve the same purpose are categorized as tissues. The four main types of tissues are muscular, connective, nervous and lining cells. | |||
=== Organs === | |||
The organs are usually located within the body, except for the skin. Examples include the hearts, lungs and [[Gospaw organ (A1-0)|gospaws]]. Many of these organs are housed in internal cavities in the body, as the abdomen, thorax, and pelvic cavity. | |||
=== Systems === | |||
==== Nervous system ==== | |||
Revision as of 19:44, 19 August 2023
The trrarrusian body is the structure of the trrarrusian being. It is composed of different cells that form tissues with different functions, which ensure the existence of the individual, its interaction with the medium and the continuation of the specie.
It comprises a head (which holds most of the sensorial organs and the central nervous system), neck, torso (which holds most of the vital organs), arms and hands, and legs and feet.
The study of the Trrarrusian bodies includes multiple branches of anatomy, physiology, microbiology, chemistry, and oology. The trrarrusian body varies in known ways, both natural and artificial. All these studies ensures vital works as the cure of different trrarrusian diseases, a better understanding of the effects of implants and prosthetics, the creation of medicines used for enhancement of capabilities and the sustained health of trrarrusians in inhospitable locations, physiological rehabilitation of injured individuals, among others.
Composition
Trrarrusians are a carbon-based specie, composed of various elements, specifically carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen, phosphorus and titanium. These elements are located in both cellular and extracellular mass.
The adult trrarrusian male body is composed of about 60% water in total, shared between extracellular fluids, blood plasma, interstitial fluids, and cellular fluids. The pH is carefully maintained rigorously, keeping a slightly alkaline pH level between 7.85 and 7.95 due to the high ammonia content required for metabolic processes. The most important electrolytes in extracellular fluids are potassium and chloride. Meanwhile, inside cells, the main electrolytes are sodium and phosphates.
Cells
Trrarrusian bodies are composed of cells. At maturity, there are roughly 59-74 trillion cells, an estimate reached with the volume of an adult trrarrusian body, the volume of each type of cell and the proportion of these cells in the body. The body also coexists with commensalist and symbiotic microorganism inside of it and on its skin, which feed on the excretion and dead cells of the individual, and in some cases serve essential roles in the body such as digestion, synthetizing of molecules and processing of atmospheric ammonia. A significant part of the total mass of the body isn't composed of cells, but extracellular tissues and material, as the protein matrix in which cells are housed, or extracellular fluids. Around 37%, or 48 kg of the 130 kg of the total mass is composed of symbiotic and commensalist organism, or non-cellular mass such as bones, connective tissues and fluids.
Genome
Cells are able to realize functions thanks to DNA. DNA in trrarrusian cells is located in a nucleus in the centre of the cells, in most cases. This DNA is used for the synthetizing of proteins within the cell, that regulate cell behaviour, metabolic processes and form structural components within and outside the cells. Some cells, as blood cells, lack DNA.
Tissues
The body is composed of multiple different kinds of cells that serve different purposes, the combination of various cells that serve the same purpose are categorized as tissues. The four main types of tissues are muscular, connective, nervous and lining cells.
Organs
The organs are usually located within the body, except for the skin. Examples include the hearts, lungs and gospaws. Many of these organs are housed in internal cavities in the body, as the abdomen, thorax, and pelvic cavity.