Mesolithic Moellia (Pacifica): Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| (7 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{History of Rhayna}} | |||
'''Mesolithic Moellia''', or '''Mesolithic Rhayna''', encompasses the mesolithic in the [[Moellia (Pacifica)|Moellia]] region from the end of the Last Glaciation Period Peak 22,000 | '''Mesolithic Moellia''', or '''Mesolithic Rhayna''', encompasses the mesolithic in the [[Moellia (Pacifica)|Moellia]] region from the end of the Last Glaciation Period Peak in 22,000 BCE, to the end of the Last Glacial Period in Moellia and the Neolithic Revolution in the current state of [[Rhayna state (Pacifica)|Rhayna]] in 11,700 BCE. | ||
The mesolithic in Moellia is characterized by the massive retreat of human groups from the interior of the region to the increasingly bigger rivers and the basin of Lake Kryo, due to the raising temperatures and change of climate as the region enters into the Holocene interglacial period. It is theorized that the pressure of the raising population density, scarcity of vegetation and retreat of large mammals to the south out of the region triggered the development of microlithic technology, proto-cultures, and a change of life-style into hunter-gatherers. | The mesolithic in Moellia is characterized by the massive retreat of human groups from the interior of the region to the increasingly bigger rivers and the basin of Lake Kryo, due to the raising temperatures and change of climate as the region enters into the Holocene interglacial period. It is theorized that the pressure of the raising population density, scarcity of vegetation and retreat of large mammals to the south out of the region triggered the development of microlithic technology, proto-cultures, and a change of life-style into hunter-gatherers. | ||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
== Cultures == | == Cultures == | ||
[[File:Rhayna mesolithic cultures.png|thumb|420x420px|Map of the general areas of the mesolithic cultures of Moellia in 12,000 BCE]] | |||
{| class="wikitable sortable" | {| class="wikitable sortable" | ||
|+ | |+ | ||
| Line 17: | Line 18: | ||
|Kaly Thea Island | |Kaly Thea Island | ||
|Kalythean | |Kalythean | ||
| | |22,000-11,700 BCE | ||
| | |Maka's Cave | ||
| | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 24: | Line 25: | ||
Continental Moellia ([[Rhayna state (Pacifica)|Rhayna]]) | Continental Moellia ([[Rhayna state (Pacifica)|Rhayna]]) | ||
|Late Dymassian | |Late Dymassian | ||
| | |22,000-11,700 BCE | ||
| | |Safi Stone Paintings | ||
| | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Katharistis Basin | |Katharistis Basin | ||
|Pylyn | |Pylyn | ||
| | |22,000-11,700 BCE | ||
| | |Lizeta Kepanta (arrow heads) | ||
| | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Imisy Basin | |Imisy Basin | ||
|Nodosian | |Nodosian | ||
| | |22,000-11,700 BCE | ||
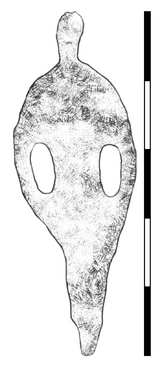
| | |[[Monera figurine (Pacifica)|Monera stance]] | ||
|Southwestern Lithic | |Southwestern Lithic | ||
Complex | Complex | ||
| Line 44: | Line 45: | ||
Moellia ([[Rhayna state (Pacifica)|Rhayna]]) | Moellia ([[Rhayna state (Pacifica)|Rhayna]]) | ||
|Assaizi | |Assaizi | ||
| | |21,000-11,700 BCE | ||
| | |Kamea (mortar) | ||
|Southwestern Lithic | |Southwestern Lithic | ||
Complex | Complex | ||
| Line 51: | Line 52: | ||
|Northern Kryo Basin | |Northern Kryo Basin | ||
|Western Mesarian | |Western Mesarian | ||
| | |20,000-11,700 BCE | ||
| | |Koryfi (pottery) | ||
|Southwestern Lithic | |Southwestern Lithic | ||
Complex | Complex | ||
| Line 58: | Line 59: | ||
|Southern Kryo Basin | |Southern Kryo Basin | ||
|Leproinian | |Leproinian | ||
| | |20,000-11,700 BCE | ||
| | |Tomonia (settlement) | ||
|Southwestern Lithic | |Southwestern Lithic | ||
Complex | Complex | ||
| Line 66: | Line 67: | ||
|North Mountainous | |North Mountainous | ||
Culture | Culture | ||
| | |16,000-8,500 BCE | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 72: | Line 73: | ||
|Apoala Basin | |Apoala Basin | ||
|Kleise | |Kleise | ||
| | |20,000-9,600 BCE | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 78: | Line 79: | ||
|Southern Moellia (Alla-gy) | |Southern Moellia (Alla-gy) | ||
|Magnakean | |Magnakean | ||
| | |21,000-11,700 BCE | ||
| | |(sculpture) | ||
| | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Western Tipo Valley | |Western Tipo Valley | ||
|Pavleronian | |Pavleronian | ||
| | |22,000-11,700 BCE | ||
| | |(pottery) | ||
|Tipo Valley Sphere | |Tipo Valley Sphere | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Eastern Bensea Basin | |Eastern Bensea Basin | ||
|Bensean Paleolithic | |Bensean Paleolithic | ||
| | |22,000-11,700 BCE | ||
| | |(pendant) | ||
|Tipo Valley Sphere | |Tipo Valley Sphere | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Eastern Moellia (Nea-gy) | |Eastern Moellia (Nea-gy) | ||
|Late Pitanian | |Late Pitanian | ||
| | |22,000-11,700 BCE | ||
| | |(weaving) | ||
|Tipo Valley Sphere | |Tipo Valley Sphere | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | |Mesaia Basin and Southwestern | ||
Mikos Basin | |||
|Mesaia Riverbed | |Mesaia Riverbed | ||
Culture | Culture | ||
| | |22,000-11,700 BCE | ||
| | | | ||
|Tipo Valley Sphere | |Tipo Valley Sphere | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | |Southeastern Mikos Basin | ||
|Mikosian | |Mikosian | ||
| | |22,000-11,700 BCE | ||
| | | | ||
|Tipo Valley Sphere | |Tipo Valley Sphere | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | |Chamilos Basin | ||
|Tanensian | |Tanensian | ||
| | |22,000-11,700 BCE | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
|} | |} | ||
== Progression == | |||
[[File:Monera stance.png|left|thumb|365x365px|Monera figure, or Monera stance]] | |||
The mesolithic in Moellia starts around 22,000 years ago with the end of the Last Glaciation Period Peak in the north of Rhayna and Nea-gy, and ends in around 11,700 BCE with the arrival of agriculture. Meanwhile, it arrives lastly to the north of Alla-gy in 16,000 BCE, and it ends in around 8,500 BCE. The end of the Last Glaciation Period Peak left little time for humans in the region to adapt as the fertile lands receded, which translated into a quick adoption of a neolithic lifestyle once agriculture was developed. The end of the Last Glaciation Period Peak also forced the once sparse populations of humans to concentrate around water sources, which is probable that it kickstarted the formation of protocultures and conflicts between groups. | |||
The lithic technology in the mesolithic is characteristic of the period, showing in the archaeological record a widespread use of microlithic technology, except for the places where the mesolithic arrived last, like the north of Alla-gy, where macrolithic technology was still used even after the arrival of the mesolithic to the zone. At the end of the mesolithic, microlithic technology was replaced by macrolithic technology, with polished stone tools. | |||
The mesolithic also presents small constructions made with astronomical or ritual significance, specially around the large rivers of the region, which could have served to predict floods and offer sacrifices. | |||
Some genetic analyses of seeds found in archaeological sites show that some humans could have ventured outside the region past the mountain ranges and come back with non-native foods, which then naturalized into the basins of the rivers and lakes. | |||
As the neolithic lifestyle spread through Moellia, the mesolithic lifestyle fell out of favour. Quickly enough, the humans of the region started cultivating in the riverbeds after each seasonal flood, formed permanent and sedentary communities around their crops, and herded animals to the mountains where the grass grew. Some populations rejected the neolithic and became nomads, who would travel the desert and raid farming communities, but with time, these communities would disappear and integrate as the sedentary populations grew larger and the climate became more relentless, although they would continue to exist past the invention of writing. | |||
[[Category:History of Rhayna (Pacifica)]] | |||
Latest revision as of 19:41, 13 April 2024
| History of Rhayna (Pacifica) |
|---|
 |
|
|
Mesolithic Moellia, or Mesolithic Rhayna, encompasses the mesolithic in the Moellia region from the end of the Last Glaciation Period Peak in 22,000 BCE, to the end of the Last Glacial Period in Moellia and the Neolithic Revolution in the current state of Rhayna in 11,700 BCE.
The mesolithic in Moellia is characterized by the massive retreat of human groups from the interior of the region to the increasingly bigger rivers and the basin of Lake Kryo, due to the raising temperatures and change of climate as the region enters into the Holocene interglacial period. It is theorized that the pressure of the raising population density, scarcity of vegetation and retreat of large mammals to the south out of the region triggered the development of microlithic technology, proto-cultures, and a change of life-style into hunter-gatherers.
Most mesolithic sites are found near water sources, although with a farther range than zones nowadays deserted, and although some of them present signs of pottery and textiles in the middle of the mesolithic, specially in the Southwestern Lithic Complex and the Tipo Valley Sphere, most settlements do not develop these technologies until the end of the mesolithic and the start of the Neolithic Revolution.
Cultures
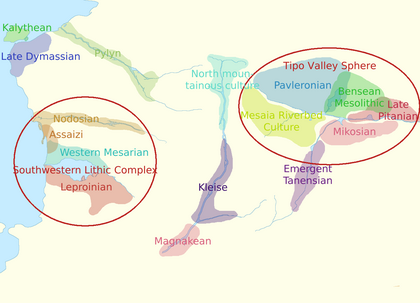
| Geographical range | Culture | Temporal range | Notable sites/artifacts | Wider region |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kaly Thea Island | Kalythean | 22,000-11,700 BCE | Maka's Cave | |
| Mount Atzali/Northwestern
Continental Moellia (Rhayna) |
Late Dymassian | 22,000-11,700 BCE | Safi Stone Paintings | |
| Katharistis Basin | Pylyn | 22,000-11,700 BCE | Lizeta Kepanta (arrow heads) | |
| Imisy Basin | Nodosian | 22,000-11,700 BCE | Monera stance | Southwestern Lithic
Complex |
| Western Continental
Moellia (Rhayna) |
Assaizi | 21,000-11,700 BCE | Kamea (mortar) | Southwestern Lithic
Complex |
| Northern Kryo Basin | Western Mesarian | 20,000-11,700 BCE | Koryfi (pottery) | Southwestern Lithic
Complex |
| Southern Kryo Basin | Leproinian | 20,000-11,700 BCE | Tomonia (settlement) | Southwestern Lithic
Complex |
| Northern Moellia (Alla-gy) | North Mountainous
Culture |
16,000-8,500 BCE | ||
| Apoala Basin | Kleise | 20,000-9,600 BCE | ||
| Southern Moellia (Alla-gy) | Magnakean | 21,000-11,700 BCE | (sculpture) | |
| Western Tipo Valley | Pavleronian | 22,000-11,700 BCE | (pottery) | Tipo Valley Sphere |
| Eastern Bensea Basin | Bensean Paleolithic | 22,000-11,700 BCE | (pendant) | Tipo Valley Sphere |
| Eastern Moellia (Nea-gy) | Late Pitanian | 22,000-11,700 BCE | (weaving) | Tipo Valley Sphere |
| Mesaia Basin and Southwestern
Mikos Basin |
Mesaia Riverbed
Culture |
22,000-11,700 BCE | Tipo Valley Sphere | |
| Southeastern Mikos Basin | Mikosian | 22,000-11,700 BCE | Tipo Valley Sphere | |
| Chamilos Basin | Tanensian | 22,000-11,700 BCE |
Progression
The mesolithic in Moellia starts around 22,000 years ago with the end of the Last Glaciation Period Peak in the north of Rhayna and Nea-gy, and ends in around 11,700 BCE with the arrival of agriculture. Meanwhile, it arrives lastly to the north of Alla-gy in 16,000 BCE, and it ends in around 8,500 BCE. The end of the Last Glaciation Period Peak left little time for humans in the region to adapt as the fertile lands receded, which translated into a quick adoption of a neolithic lifestyle once agriculture was developed. The end of the Last Glaciation Period Peak also forced the once sparse populations of humans to concentrate around water sources, which is probable that it kickstarted the formation of protocultures and conflicts between groups.
The lithic technology in the mesolithic is characteristic of the period, showing in the archaeological record a widespread use of microlithic technology, except for the places where the mesolithic arrived last, like the north of Alla-gy, where macrolithic technology was still used even after the arrival of the mesolithic to the zone. At the end of the mesolithic, microlithic technology was replaced by macrolithic technology, with polished stone tools.
The mesolithic also presents small constructions made with astronomical or ritual significance, specially around the large rivers of the region, which could have served to predict floods and offer sacrifices.
Some genetic analyses of seeds found in archaeological sites show that some humans could have ventured outside the region past the mountain ranges and come back with non-native foods, which then naturalized into the basins of the rivers and lakes.
As the neolithic lifestyle spread through Moellia, the mesolithic lifestyle fell out of favour. Quickly enough, the humans of the region started cultivating in the riverbeds after each seasonal flood, formed permanent and sedentary communities around their crops, and herded animals to the mountains where the grass grew. Some populations rejected the neolithic and became nomads, who would travel the desert and raid farming communities, but with time, these communities would disappear and integrate as the sedentary populations grew larger and the climate became more relentless, although they would continue to exist past the invention of writing.