Livana (Pacifica)
The Confederacy of Livana Coniuratio Livana | |
|---|---|
Motto: Victory in Freedom Uictoriae Fiducia | |
Anthem: March of Victory Victoria Martii | |
 Location of Livana in the South Pacific | |
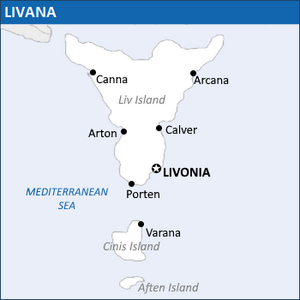 Enlarged map of Livana | |
| Capital and largest city | Livonia |
| Official languages | Livanan |
| Recognised regional languages | Austral |
| Religion (2020 census) | 91,38 Cultus Rationem 4,75% Other 3,87% None/Non-specified |
| Demonym(s) | Livanan |
| Government | Semi-Presidential Bicameral Federal Republic |
| Peter Trenton | |
| Dwight Raleigh | |
| Legislature | Parliament of Livana |
| College of Seers | |
| College of Representatives | |
| Independent state | |
• Years of Insurrection | 1824 - 1848 |
• Article of Confederation signing | 26 September 1848 |
• Fall of Colonel Tarsis | 10 January 1980 |
| Area | |
• Total | 11,574 km2 (4,469 sq mi) |
| Population | |
• 2021 estimate | 6,856,721 |
• 2020 census | 6,842,052 |
• Density | 592/km2 (1,533.3/sq mi) |
| GDP (nominal) | 2020 estimate |
• Total | $ 203.533 billion (₣847.61 billion) |
• Per capita | $ 29,683.72 (₣123,617.78) |
| Gini (2020) | 35.2 medium |
| HDI (2020) | very high |
| Currency | Fera (₣) (FEA) |
| Time zone | UTC+2 |
| Date format | dd/mm/yyyy CE |
| Driving side | left |
| Calling code | +197 |
| World Forum Code | LV |
| Internet TLD | .lv |
Livana (Livanan pronunciation: [li.vaa.nuh]), officially the Confederacy of Livana (Livanan: Coniuratio Livana, Livanan pronunciation: [ko.nyu.ra.tyo li.vaa.nuh]) is a country in the Mediterranean sea. It is located at the crossroads of the Mediterranean Sea and the Bailtem hinterland, which have contributed to its rich history and shaped a distinctive cultural identity and religiosity. It is part of the Bailtem region of the South Pacific. Livana is home to roughly six million people and covers an area of 11,574 square kilometers (4,469 sq mi), making it one of the smallest countries in Bailtem. The official language of the state is Livanan, while Austral is also formally recognized.
The earliest evidence of civilization in Livana dates back over 5,000 years ago, around the beginning of recorded history. Modern-day Livana was home to the proto-Livanans, a culture that flourished for almost 1,000 years (c. 3,000 BCE–1,000 CE), before being assimilated into the Tolosan colonists around 1,000 BCE. Between 1,000 BCE to the 5th century CE, the archipelago became a major outpost for the Tolosan Republic, centered in today's Stoinia. After the sacking of Tolosa in the 5th century, the islands fell under anarchy until being forcefully unified under the leadership of Foramil the Conqueror while the modern Livanan language began to take shape. The death of Foramil marked the beginning of the Middle Ages in Livana as new kingdoms and fiefdoms emerged from his domain. Livonia eventually grew into the islands' population center, while Arcana expanded into a massive commercial power dominating the Mediterranean Sea until its decline in the 16th century.
The fiefdoms eventually formed four separate states by the 16th century, the Kingdoms of Arcana, Canna, and Cinis, alongside the Theocracy in Livonia. Following the Great Liv War in 1675, the High Priest no longer exert tremendous influence beyond Livonia and the islands descended into a state of anarchy between the four kingdoms. Throughout the 18th century, enlightenment ideals were brought into the islands, culminating in the Livonian Revolt of 1837. Upon the establishment of a democratic republic in Livonia, the islands experienced constant strife and warfare, until the end of the Royalists War in 1848 and the dissolution of the four kingdoms into a united Republic of Livana. Stability was finally achieved and Livana progressed through the industrial revolution, becoming an influential player in the Mediterranean Region as well as across Pacifica. The booming period ended with the breakout of the Livanan Civil War in 1951 which saw the rise of the authoritarian Tarsis Regime, a military dictatorship under Colonel Tarsis Vitruvia. Democracy was restored in 1980 during the January Uprising, which also transformed Livana into a Semi-Presidential Confederation.
Livana is a well developed country, ranking quite high on the Human Development Index and among the highest in Bailtem outside of the large economies of the Western Mediterranean. It has been classified as an upper-middle-income state. However, the Livanan economy is plagued by colossal public and foreign debts, as well as instances of corruption. Political divisions left from the Tarsis Regime also contributed to the high number of domestic political violence that has claimed 26 high-ranking political officials in the last 50 years. Despite the country's small size, Livanan culture is renowned both in the Mediterranean and globally, primarily powered by its extensive tourism industry. Livana is a member of the World Forum, the International Labor and Trade Council, and a founding member of the Cross Mediterranean Economic Community (CMEC).
Etymology
The name Livana originates from the Cinaian dialect root 'Liveant' meaning “lively”, apparently a description of its largest landmass, Liv Island which also has the same name origin.
Occurrences of the name Liv have been found in writings since before the Cinaian unification, with Cinaian Tolosans referring to the main island as "Liv" as far back as the 2nd century CE. The name is recorded by ancient Mediterranean explorers to describe the archipelago as a whole. By the 12th century, the name Livana was already quite prominent, thanks to the increasing influence of the Cultus Rationem, driven by Livonia. In 1848, during the conference to establish the republic’s first constitution, representatives agreed to adopt Livana as the official name of the nation.
History
Main Article: History of Livana
As part of the Mediterranean region, Livana was influenced by numerous succeeding empires throughout ancient Mediterranean history, predominantly empires and polities from Bailtem and the western parts of the sea. Livanans are descendants of the proto-Livanan civilization and Tolosan colonists between 800 BCE to the 5th century CE. The collapse of the Tolosan civilization brought Livana into an era of warlords, which ended with the conquest of Foramil.
Between the 8th century to the 16th century, the archipelago was marred by feudal anarchy, but beheld the rise of Arcana as a naval power dominating the Mediterranean Sea. The doctrine of absolutism reached the islands as four nations rose in the 17th century which ended the feudal anarchy. Arcana, Livonia, Canna, and Varana, each fought wars against one another until the Revolution in the 19th century united the Iislands into a single Republic. Democracy flourished in Livonia all the way to the breakout of the Livanan Civil War in 1950, and the rise of the Tarsis Regime. Amber Lyson's reformist movement ended the dictatorship and created the current Confederation.
Proto-Livanan and Tolosan Civilization

Main Article: Tolosan Republic
First instance of civilization in Livana dated back to 3,000 BCE through analysis of ruins in Southern Liv. The so-called pre-Tolossan Livanan society exists primarily as neolithic tribes, focused on farming and fishing. This early civilization boasted a marine livelihood and some of the earliest settlements were built along the coasts. These tribal polities was loosely organized, but united through basic commerce and trade. There were no writing system during the time, but some cave murals and monoliths depicted some legendary rulers that conquered large swathes of the archipelago, but none ever united the islands under a singular polity. These people were assimilated completely when the Tolosans began their colonization of the archipelago.

The Tolosan Republic began their expansion throughout the Mediterranean regions around 800 BCE, establishing multiple colonies in what is today modern Spiras, and eventually arrived in Liv Archipelago. The first settlement was constructed in the southern tip of Liv Island, and later would become the primary Tolosan city of Hiron. Further settlements and colonies were built along the eastern and western coast of Liv, and in Cinis. Eventually, Livana became a primary outpost of the Republic, and its population grew. The Tolosan brought with them their maritime technology, architecture, and agriculture system. Many of today's fertile lands in Northern Liv was opened and developed by the Tolosan during their hegemony, helped by the construction of aqueducts and canals that still survive to modern times.
In 427 CE, Tolosa was invaded and destroyed by proto-Ezervulgish invaders, causing the collapse of the Tolosan republic. In the Liv Archipelago, the absent of Tolosan garrisons brought anarchy as local warlords from the colonies rose up and began an era of anarchy that lasted for almost two hundred years. The population of the archipelago plummeted and there were little written historical accounts of this era.
Cinaian Conquest
Main Article: Conquest of Foramil

Around 782 CE, Foramil The Conqueror crossed the Cinaian Strait and laid siege to Hiron. Foramil was largely an unknown leader in Liv up to that point, however he and his father had united the disparate Tolosan warlords in Cinis, and formed a prosperous domain centered in the city of Beruna (now modern Varana). He eventually laid siege to Hiron which lasted for almost a year, while his sons was given commands to conquer the rest of Liv Island. Foramil was almost defeated by a united force of several city-states allied with Hiron in the Battle of Gurther in mid 783 CE, but managed to prevail and eventually, won the siege. After the fall of Hiron, Foramil conquered all city-states that in Liv, uniting the archipelago once more. Foramil would went on to rule over the united archipelago for fourty years, ushering in an era of peace and stability. During this time, the Livanan language in its modern form began to take shape as it drifted further from its Tolosan roots.
Foramil died in 823, on the 40th anniversary of his conquest of Hiron. Unfortunately, his realm ended with his death as his sons and generals began to quarrel over his domain and splintered it apart into multiple smaller realms. The archipelago was thrown once more into anarchy that persists until the 12th century.
The Middle Ages and the Renaissance
Main Article: Livanan Renaissance

Following the collapse of Foramil's realm, the islands was divided once more. Hiron was sacked by one of the descendants of Foramil in 961 CE, forcing the population to find shelter in another area to the east, which would eventually grow to become the City of Livonia. Between the 9th and 12th century, old Tolosan cities reemerged as regional powers, such as Arcana, Canna, and Varana. In Livonia, the former High Priest of Hiron organized a theocratic curia within the city around the year 1011 CE. Livonia eventually became a center of trade and culture protected by the Church, offering a save haven for trade barges sailing through the Mediterranean Sea. Around the 14th century, Austral influences from the mainland began to infiltrate the archipelago, brought by traders and foreigners that visited the archipelago, eventually transforming Livanan language to its modern form.

In the hinterlands, feudalism began to take shape as local lords offered lands in exchange for protections. Small fiefdoms rose up around local lords and noblemen, while the Church became a dominant force over these lords, providing them with legitimacy and literate clerks, while their holdings grew across the archipelago. Livonia became the center of this new era. Even though wars between these fiefdoms were widespread and often, the stability provided by the Church led to gradual population recovery throughout the islands. Between the 13th and 14th century CE, most of the smaller fiefdoms have been annexed or integrated to larger Kingdoms. During this era, Kings and noblemen began to sponsor art and cultural achievements, ushering in the Livanan renaissance. The Kingdom of Arcana, Valera, and the Republic of Calver became centers for this artistic and scientific movements, eventually growing to prominence and even rivaled Livonia in size and wealth.

Kingdom of Arcana
Main Article: Kingdom of Arcana
In 972 CE, Lord Marvinus of Galeta was driven out of his domain by the Kingdom of Canna. He and his subjects seek refuge in a small island in the middle of a lagoon near the northeastern peninsula of Liv Island, built on wooden pillars to support it above the swampy ground. This settlement eventually grew into the City of Arcana, and would became a center of trade and manufactories in the Mediterranean Sea. In 1215, in the middle of a war with the nearby Republic of Calver, King Septimus VI ordered the construction of the Arcanan Arsenal, a massive dockyards that helped grew Arcana's naval power.

Arcana was transformed into a trading empire that spanned the entirety of the Mediterranean Sea, dominating trade and guarding merchants from pirates for the next two centuries before it began to stagnate. Arcanan colonists settled the Virin Island in the 1400s, and built the city of Castra Regina in honor of Queen Anna I "The Virgin Queen". Arcana settlements in Northern Bareland eventually grew and become densely populated. The Great Civil War of 1670 ended with the secondary house from the Galeta Dynasty, House Eria founding the Kingdom of Eria. The war left the Royal Fleet severely weakened. Arcana was eventually outcompeted by other emerging cities and nations around the Mediterranean Sea in 17th century.
Unification of Livana
By the 18th century, many feudal lords had lost their influence, and four cities dominated the island chains. The Kingdoms of Arcana, Canna, Cinis, and the Theocracy of Livonia became the only polities still execerting great influence. The dual system between feudal lords and the theocracy was already defunct, evidently after the Great Livanan War in 1782, which was a war of succession dispute between an alliance of Cinis and Canna against Arcana. The war exposed bitter feuds between the nobilities, showcasing the Archpriest's declining influence over the isles. This bitter feuds came in a time of interconnection and the resurfacing of a Livanan identity, which was decaying since the death of Foramil. Arcana went into another war with Canna in 1833 which lasted for four more years.
Great Livanan Wars

Main Article: Great Livanan Wars
A succession crisis started in Arcana after the death of the last Galeta Dynasty monarch, King Georgius II in 1777. The closest relative to the late king was his cousin, the reigning King of Canna, Luther X claimed the throne of Arcana and invaded the Kingdom in January of 1778. Livonia supported the ascension of Queen Margareta, the late king's wife to the throne and demanded Canna's withdrawal from Arcanan territory. King Luther X refused and went on to march on Arcana, but was held in the trenches near Alghero. A stalemate ensued while Cannan and Arcanan fleet battled across the sea. In December of 1779, Livonian forces managed a breakthrough and nearly captured the city of Canna, when a fleet of Cinaian ships landed thousands of Varanan reinforcement in the city bolstering Canna's defence and defeating the encroaching Livonian forces.
A royal marriage was secured between the royal houses of Canna and Cinis just a month before the Battle of Canna. The stalemate was finally resolved when Queen Margreta died of assassination in 1782, and a coup in Arcana brought the regency council to power in Arcana. Canna agreed to accept the regency's temporary control over Arcana, and promised to obliged to the council's decision on who will ascend the throne in Arcana. A truce was signed in 24th December 1782. The council began to took over Arcana as an oligarchic entity, taking over crucial state institutions and many of the royal's original duty. In 1832, the council finally elected a king from amongst their ranks, King Paulus III of House Genna. The decision was not received well by the new King of Canna, Luther XI, who promptly invaded Arcana once more. Cinaian ships put the island into a long blockade, while Livonia elected to stays neutral. The war eventually ends when the Theocracy in Livonia was overthrew in a revolution.
Livonian Revolution

Main Article: Livonian Revolution
The so called Livonian Uprising happened due to many causes, but it was mainly due to the failure of the Archpriest to prevent another war between Arcana and Canna. The war dealt a negative effect on Livonia; stopping food supply and other essential goods. The city was on the brink of famine, and the Archpriest began to pay foreign merchants for food. In 1833, Livonian Merchant Guild banded with the Craftsmen Guild and petitioned the Archpriest at the time, Nicolaus XII, to found the People's Council with 40 members from both guilds to manage and help the payment for foods and clothing. Nicolaus XII accepted the offer, and the new council was summoned, elected by the people of Livonia and the theologians in the very first election of Livana, the Election of 1833. The council poured money collectively, and managed to levied the city out of the dire situation.

When the war ended, Nicolaus XII demanded the People's Council to be dissolved, citing that its work was already done. However, the council rebuked the Archpriest's request and then posted newspapers in defiance of Nicolaus XII's demand. The Theocracy began to amass the Holy Guard to the city, and on 16th of June 1837, the guards attacked the Council's meeting hall (today's Caifre Exhibition By-The Sea, killing at least twelve men, and arresting the rest of the counselor. The attack enraged the people, and on 17th of June, a huge mob gathered around the Hiron Cathedral, demanding the rest of the counselors to be released, and that everyone involved in the murders is sentenced. The mob gathered for about three hours, before a cavalry contingent of the Holy Guard charged them in the Theocratic Plaza. However the mob was armed as they was organized by the Merchant Guild which bought the armaments. The cavalry charge was repulsed, and the mob stormed the cathedral. The event that would colloquially known as the Livonian Uprising, saw Nicolaus XII and many members of the Theocracy arrested, while the Holy Guard disbanded. The theocracy was dissolved after Nicolaus was tried on 20th of June, and imprisoned.
Revolutionary War

Main Article: Livanan Revolutionary War
Soon after the Livonian Uprising, Arcana and Canna ceased their fighting and formed the Holy Alliance to restore the Archpriest. A holy war was declared by the Alliance, and Arcanan forces were the first to arrive in the periphery of Livonia on July 28th. The forces quickly surrounded the city and began laying siege. The siege lasted for one month without any advantages gained by the Arcanan forces. During the duration, Livonia declared the founding of the Citizen Republic on July 30th and conscripted the male populace of the city to repulse the siege. On August 26th, an Arcanan fleet attacked the Livonian Harbour, but was quickly defeated by the Livonian fleet which mainly consisted out of the city's merchant ships, in the Battle By The Sea. The defeat discouraged the Arcanan forces which withdrew the next day. The Livonian forces advanced behind the withdrawing Arcanan forces, and clashed in the first land battle of the war, Battle of Calmer on September 2nd, 1837. The Livonian won the battle, and scattered the Arcanan forces with limited casualties, mainly due to the brilliant strategy of Citizen-General Andre Guilles. Amongst those killed in the battle was King Paulus III of Arcana.

The victory at Calmer threw Arcana into political disarray. The Arcanan heir, Paulus IV, was a five-year-old boy and was heavily influenced by the royal court. Arcanan citizen and guild, which were already in contact with the Citizen Republic, staged an uprising on September 10th, 1837, coinciding with Paulus IV's ascension. The uprising was crushed, however, and Arcana was put into military administration while young Paulus was transported to Hurtie, a town 6 miles north of the city. The regent of Arcana, Duke Halicar of Hurtie took control of the kingdom and re-amassed the Arcanan army. When the Livonian forces finally arrived in Arcana in late October (a delay happened during the march north), their troops were defeated by the Arcanan. In December, Cannan troops finally reinforced the Arcanan and together pushed the Livonian back to the south.
On January 12th, 1838, Livonian forces led by Andre Guilles received reinforcement from Livonia, and finally stopped their retreat. They formed a defensive line near Gutthingen Village and camped through the night. In the morning of January 13th, the Alliance forces, led by the King of Canna, Luther XI and Duke Halicar arrived on the battlefield. The Battle of Gutthingen lasted for six hours, and resulted in 20,000 deaths on both sides. Andre Guilles' superior tactics were credited as the Livonian won the war, capturing both King Luther and Duke Halicar. The victorious Livonians marched north and arrived in Arcana by February 2nd. They captured King Paulus IV the next day, effectively ending the war. All nobility in Arcana and Canna was dissolved, and both kings are held under house arrest in Livonia. Arcana declared a Citizen Republic on February 16th, 1838, while Canna declared their republic after the Livonian forces arrived in the city and took it without any resistance on March 10th.
Republican Era
Royalist War
Main Article: Livanan Royalist War

The three Citizen Republics of Liv survived for another 10 years since the Battle of Gutthingen. In 1839, Livonia allowed the theologians to form a religious administration in Hiron Cathedral, but solely for religious purposes, and was restricted from any political power or influence over the republic. Nicolaus XII was not allowed to be put forward as a candidate for High Priest, and died in house arrest on July 1840. In 1845, the then teenage Paulus IV escaped his house arrest and ran to Cinis. The news of his escape insinuated a Royalist Uprising in Arcana on April 1845. The uprising turned into a full blown war, when Paulus IV returned to Arcana with a huge Cinaian Fleet led by King August II of Cinis.

The Royalist forces defeated the Republicans of Arcana and forced the Council of Arcana to flee into Livonia. On June 2nd 1845, the council of Arcana and the Arcanan Republican troops was incorporated into the Livonia Citizen Republic. Livonia marched north and defeated the Royalist-Cinaian forces in the Battle of Caltroupe on June 15th. Arcana was retaken, and on the ensuing chaos, the thirteen year old Paulus IV was murdered. The war then entered a stalemate. Even though Arcana was amalgamated into Livonia, Cinis never sues for peace until later in the war. The stalemate ended in July 6th 1848, after the merchant guild of Livonia hired mercenary ships and used them to land republican forces on Cinis. The landing was uncontested, and King August II surrendered the next day. By August, Livonia controls the entirety of the isles except for Canna. In a declaration of unison made by the council of Canna on August 28th, Canna gave up its independence and was amalgamated into the Livonian Citizen Republic. The Citizen Republic was finally dissolved in September 26th after the signing of the Article of Confederation which declared the creation of the new Republic of Livana.
Old Republican Era
Main Article: Republic of Livana

Throughout the 19th and early 20th century, Livana entered into an era of stability and growth. Commerce returned to the isles, as the Mediterranean Sea gained newfound importance with the rise of nation states. Arcana and Canna undergone significant architectural renovations which altered the city's skyline into the familiar shape they have now. The very first skyscraper in Livana was built in Livonia in 1926, the Ephenereal Building which was opened during the Livanan Exhibition of 1927. Following its construction, Livonia's skyline transformed into a jumble of highrises and dense residences. The railroad network connects the three cities of Liv, offering lanes for commercial as well as industrial purposes. Across the Cinaian Strait, the city of Varana saw an explosion of population as Liv populace as well as migrants moved into the city to work in its coal and ore mining industries which were very lucrative at that time of industrial expansion. Coal mining and iron smelting businesses boomed in Cinis, as ores were frequently discovered in abundance throughout the island. The then newly constructed Cinaian ferry harbor which was finished in 1865, eased migratory movement into Cinis, further increasing its population.

In Northern Liv, the republic renovated the old Grand Aqueducts with steam machinery, improving the irrigation system in the whole region and practically doubled food production by 1900. Food abundance led to exceptional population growth throughout the 19th century. The population of Livana doubled in mere 30 years between 1880 to 1910. The industrialisation of Livana was followed with the introduction of electricity and phone. In 1918, foreign made cars entered Livanan markets, and by early 1920, Livana is in dire need of paved roads. The government carried many infrastructure projects through the '20s and '30s, including road paving and asphalting, airport constructions, and new ferry services.

Livonia's city government built Livana's first subway tunnel in 1922 that run through between Old Livonia and Canis Market. When the project was finished in 1924, similar projects were already on construction in Canna and Arcana. The nation was seen as an emerging power in Pacifica and heavily engaged in trade. Livana was experiencing its first economic golden era under a democracy. Due to its proximities and strategic location within the Mediterranean Sea, Livana was able to export its productions efficiently, leaving businesses and the government in surplus account every year. However, in the later years of the 20th century, the dangerous and repulsing patronage system of Livanan politics and businesses circles of these eras was exposed, ending the economic expansion altogether.
Livanan Civil War

Main Article: Livanan Civil War
Democracy in Livana continues uninterrupted until the 1950s, when a corruption scandal involving the majority of the government, the Vizier Scandal was uncovered. The scandal involved almost the entire breadth of the Livana government, and was revolving around money laundering operations for bribery and corrupted money through Vizier Harbor in Varana. The investigation was led by the journalist Adam Saunders whom was murdered after his reports were made public. His murder led into an uproar throughout Livana, while in Livonia, a massive protest in June 16th 1950 errupted into a chaotic shoot out with Livanan police (the day now known as the Bloody June), which killed at least 200 protesters and 15 polices.

President Hunters enacted an emergency decree the day after the riots and martial law was put into effect in Livana's biggest urban centers. The effects of the martial law were not good for Livana's economy, as investors began to withdrew their investments from Livana. Livana filed for bankruptcy in late 1950, and famines began to reappear in the cities. Shortages was confounded with the advent of the Great War which only made Livana's fragile stature worsened. On January 1951, a group of students from the University of Arcana raided local infantry barack and stole armaments including some tanks and artillery pieces (possibly with help from a traitor inside the government). Their action sparked the conflict that would be known as the Livanan Civil War.

The civil war was fought between President Hunters' Nationalist, and the Freedom Fighters (FF) which was led by a former Arcanan activist and professor, Andreas Willington. The FF grew from around 500 militias into more than 20,000 personnel during the course of the conflict, while mutinies were abounds in the Nationalist's forces whom often disobeyed orders of shooting their own countrymen. The war was mostly guerilla in fashion, fought within the forests and hills in the foot of Mount Carna. Some rebel factions also fought in Cinis. The FF manages to capture the entirety of Aften in September 1951, and was in control of most of Liv and Cinis' interior by that time. The war took a drastic turn after the FF, with help from the mutiny of the 12th Varana Regiments led by Colonel Tarsis Vitruvia, defeated the Nationalist and took over the city of Varana on 22nd of February 1952.
Tarsis soon became the leader of FF following the death of Andreas Willington on February 27th. On March 1st, President Hunters escaped Livonia by the sea, but was captured by a rogue FF vessel, just 4 hours after his departure. He was promptly killed by the rogue sailors whom then dumped his body to the sea. Vitruvia and FF forces marched into Livonia on March 3rd, ending the war. In the end, there were around 5,000 military casualties, and up to 12,000 civilian one, mostly dealt by the Nationalists. The FF however was also accused of war crimes, especially during the capture of Arcana when women and children harassments were reported.
Tarsis Regime
Main Article: Tarsis Regime See Also: Tarsis Vitruvia

Vitruvia was sworn into office by the new FF government of Livana on March 5th 1952, with Amber Lyson one of FF speakers as his vice president. His ascension was met with enthusiasm in Livonia and Arcana, while sentiments for the Nationalists were still around in Cinis and Canna. The Tarsis Regime would go on to rule over Livana for the next 27 years with almost no power limitation. Vitruvia's hold over power began to grow after his first year as president when he dissolved the FF-filled parliament in 1953. He then formed the Conservatives and made the new party his new power basis. This antagonized the FF, which attempted a silent coup in December of 1953. The coup failed, and most FF leaders and members were imprisoned. Those who didn't get caught in Vitruvia's purge emigrate from Livana. Throughout the remainder of the '50s, Vitruvia's so-called Tarsis Regime rebuilt the countryside, and revitalize the infrastructure, while at the same time suppressing media freedom and restricting civil rights.

The Tarsis regime brought temporary stability and 10 years of economic progress and recovery. The Conservatives were soon joined by the Labour and Worker Party, consisting mostly of Vitruvia's allies in the workers union throughout the country. This party acts as the opposition, although they rarely defied the Conservatives, let alone Vitruvia. A more radical party, the Syndicalist Party formed in 1965 but was soon forced to disband in 1966. The party only exists illegally throughout the rest of the Tarsis Regime. Many syndicalists went on to be Labour MPs while secretly bringing leftist leaning to the parliament. By 1974, Livanan national politics has become partisan and factionalized once more, and Vitruvia's hold on the legislative seemingly waning. The President's own health became questioned after he began to constantly cough, as he was a heavy smoker.

Livana's economy maintains its momentum until 1979. The government nationalized the Mediterranean Marble Mining company into the National Aften Mining in January 1976. The Tarsis Regime had been reliant on foreign investment and was heavily indebted to many Bailtem countries. The nationalization and the growing factionalism in Livana drove many investors away from the country, forcing Livana to take more debts by 1977. Livana fell into another bankruptcy in December 1979, finally unable to cope with its own debts. A massive protest broke in the nation, on the so-called January Uprising in January 1980. Five students from the University of Arcana were brutally murdered by riot police on January 5th. The murders led to mass hysteria in Arcana throughout January, where approximately 15 people were killed. Vitruvia was on a trip abroad and was unable to act flexibly as if he was in Livonia. around 10,000 Livonian protesters occupied the Livanan Parliament, demanding Vitruvia and his cabinet to stand down. The gathered students in Livonia founded the Freedom Faction on January 7th. The Faction arrested Vitruvia when he landed in Livonia on January 10th under charges of embezzlement and human rights abuses, together with several murder charges which were never proven to be true. The President was pending his impeachment trial when he was killed during the Livonia General Prison Fire on March 10th.
Transition to Confederation

Amber Lyson was sworn in as the new President and was mainly inactive through his tenure, leaving the Great Reforms to the newly created title, Prime Minister of Livana. Jeremy Clinton was the first Prime Minister elected by the parliament. The new Livanan Constitution of 1983 was approved after a brief period of emergency government. The enactment of the new constitution reformed Livana as a confederacy, and saw the drastic reducing of the president's powers, and a new balanced look with greater emphasis on the parliament. New bureaus was established to overlook the government's conduct, while the power to appoint Supreme Court Justices are now in the hand of the PM. After Lyson's tenure ended in 1985 due to the newly put term limit, the Freedom Faction founded the Liberty Coalition with the Conservatives, winning elections in 1990, and 2000. In 2005, the People's Coalition finally won its first election, and won another in 2010, before losing the election in 2015.
This era following Lyson's resignation is known as the Reformation Era, and its still considered as the current socio-political era in Livana. The government concentrated on restoring living condition and prosperity to Livanans. Many modernisation program ensues, and Livana's condition economically was restored to pre-1979 level in 2000. However, due to the final years of the Tarsis Regime, Livanan politics is now dangerously factionalized, and with the advent of paramilitary groups throughout the nation, without any restriction on their political alignment, political violence could potentially erupts once more.
Zholtiya Crisis and Pelinai Civil War
Main Article: Pelinese Civil War
Geography

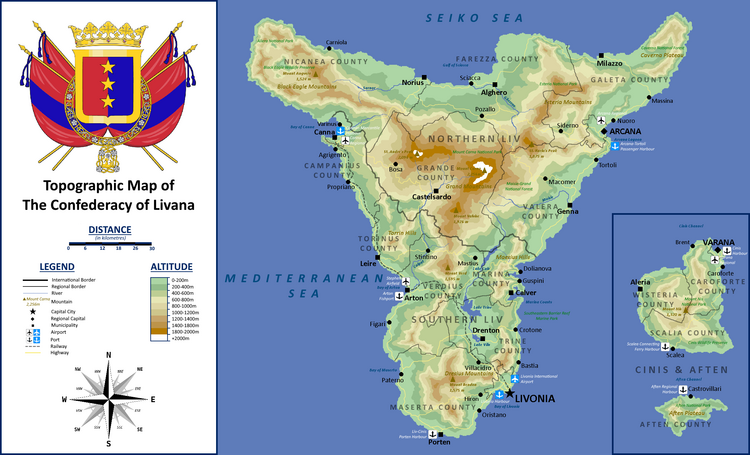
Livana is located in Southern Bailtem between latitudes 27,5° and 28,9° S and longitudes 36,5° and 37° E. Its land straddles the confluence between Bailtem and Bareland Plates. The country's surface area is 11,574 square kilometers (4,469 sq mi). Livana has a coastline and border of around 600 kilometers (373 mi) on the Mediterranean Sea. Livana is divided into three distinct physiographic regions: the coastal alluvial plain, the volcanic regions, and the staggered highlands.

The narrow and discontinuous coastal plain stretches around the islands’ coasts. In Liv, the plain expanded in Northern Liv and narrowed on the eastern and western sides of the island. The fertile coastal plain is formed of marine sediments and river-deposited alluvium alternating with sandy bays and rocky beaches. Livana’s mountains rise steeply parallel to the Mediterranean coast and form a ridge of limestone and sandstone that runs for most of the country's length. The mountain range varies in width between 10 km (6 mi) and 56 km (35 mi); it is carved by narrow and deep gorges. The range’s highest peak stands at 2,256 meters (7,401 ft) above sea level in the volcanic cone of Mount Carna in the center of Liv Island and gradually slope to the south before rising again to a height of 1,575 meters (5,167 ft) in Mount Rendon. The Meridian valley sits between the highlands in central Liv and Mount Redon in the south; it is a part of the Mediterranean Rift system. The valley is 52 km (32 mi) wide and its fertile soil is formed by alluvial deposits. The Northern range runs parallel to Liv’s northern coastline, its highest peak is St. Maud's Peak at 1,584 meters (5,196 ft).
The mountains of Livana are drained by seasonal torrents and small streams that empty into the Mediterranean Sea. Livana has no permanent rivers, and most bodies of water inland are manmade; hundreds of waterfalls exist among the ranges in Liv, and quickly drain into irrigation canals or straight to the sea.
Climate
Livana has a moderate Mediterranean climate. In coastal areas, winters are generally cool and rainy whilst summers are hot and humid. In more elevated areas, temperatures usually drop below freezing during the worst winters with snow cover on the mountains that remains until early summer on the higher peaks. Although most of Livana receives a relatively large amount of rainfall, when measured annually in comparison to its arid surroundings, northern Liv receives the most of the rainfall, mostly because of the rain shadow effect caused by the mountains in the central part of the island.
Environment

In ancient times, Livana was covered by large forests of cedar and alpine trees. Millennia of deforestation have altered the hydrology in the mountains of Liv and changed the regional climate adversely. As of 2012, forests covered 13.4% of the Livana land area; they are under constant threat from wildfires caused by the long dry summer season.
In 2010, the Ministry of Forestries and the Environment set a 10-year plan to increase the national forest coverage by 20%, which is equivalent to the planting of two million new trees each year. The plan, which was funded by both government and private investments through the Livanan Reforestation Initiative (LRI), was inaugurated in 2011 by planting cedar, pine, wild almond, juniper, fir, oak, and other seedlings, in all three states of Livana. As of 2016, forests covered 13.6% of Livana, and other wooded lands represented a further 11%. Since 2011, over 600,000 trees, including cedars and other native species, have been planted throughout the country as part of the Livana Reforestation Initiative (LRI). However, the protection of these newly planted trees is still being debated, and many replanted trees were cut down again after it has grown into considerable size due to the lack of legislative protection.
Livana has three significant protected natural reserves; Cinis Nature Preserve in Cinis Island, Aften National Park in Aften Island, and the Black Eagle and Avian Reservation in Northern Liv.
Government and Politics

Livana is a representative democracy organized as a federal, semi-presidential republic. As one of the earliest republics of the modern world, democratic traditions and values are deeply rooted in Livanan culture, identity, and politics. The Constitution of the Confederacy was approved by referendum on 1st of March 1980, establishing a framework consisting of executive, legislative and judicial branches. It sought to address the instability of the former Republican government by combining elements of both parliamentary and presidential systems, whilst greatly strengthening the authority of the legislature relative to the executive.
The executive branch has two leaders. The President of the Confederacy, currently Peter Trenton, is the head of state, elected directly by universal adult suffrage for a five-year term. The Prime Minister, currently Dwight Raleigh, is the head of government, elected by the Parliament to lead the government. The President serves as Chief of the Armed Forces and the High Commissioner of the National Police, and also have many theoretical powers attached to his duty, including vetoing legislations and announcing decrees, though these powers are rarely used. The Prime Minister has the power over domestic and foreign policies while also oversees the execution of legislations through the civil service. The Prime Minister also has powers to appoints Supreme Court judges. Both serve for a single five-year term and can only be re-elected once.
-
Peter Trenton, Incumbent President of Livana
-
Dwight Raleigh, Incumbent PM of Livana
-
Tilda MacDonald, Incumbent Minister of Interior
-
Joshua Gavinius Cicero, Incumbent Minister of Defense
-
Marius Garlan, Incumbent Minister of Foreign Affairs
Legislative

Main Article: Parliament of Livana The legislature consists of the Parliament of Livana, a bicameral body comprising a lower house, the College of Representative (Collegium Legatorum), and an upper house, the College of Seers (Collegium Vatum). Legislators in the College of Representatives, known as MPs (Consulum), represent local electoral districts and are directly elected for five-year terms. The College is led by a Collegiate Speaker, elected from among his MP peers, although usually came from the governing coalition. The College have powers to legislate, as well as to approve government budget and ratify international agreements. Seers are appointed by governors to represent state governments in the national legislation, acting mostly as an advisory body to the College of Representative and to the Cabinet. In the event of disagreement between the two chambers, the College of Representatives has the final say.
Until the Civil War, traditionalism was a strong political force in Livana, embodied by the Conservative Party which was the most important party of the Republic. Since the fall of Tarsis, they were marginalized while Livanan politics became characterized by two politically opposed groupings: one left-wing, centered on the Workers and Labours Party; and the other centrists, centered on the Liberal Faction until 2015 when the Workers and Labours Party became the dominant force, overtaking both the Conservatives and the Liberals after forming the People's Coalition with the more radical Syndicalist and Green Party. A historic snap election was called in 2023, caused by the Green Party's departure from the coalition, which resulted in the fictory of the Forward Coalition led by the Liberal Party.
Law and Order

The Livanan legal system is based on the civil law system, with the exception of matters related to personal status (succession, marriage, divorce, adoption, etc.), which are governed by a separate set of laws designed for adherents of the Cultus Rationem (which are accommodated by the Court of Morality(Atrium Moralium)). The Livanan court system consists of three levels: courts of the first instance, courts of appeal, and the court of cassation. The Supreme Court rules on the highest level of cases, including constitutional disputes and electoral problems. There are five Supreme Court Judges, all appointed by the Prime Minister from a pool of candidates proposed by the College of Representative.
In 1980 article 95 was amended to provide that the parliament shall take necessary measures to abolish political structure based on religious affiliation, but the Cultus Rationem adherents overwhelmingly supported the maintenance of a separate religious court, the Court of Morality, to handle personal and religious affairs for their adherents.
The National Police is organized in parallel with the court system, consisting of three levels; district (in Counties)/ward (in Municipalities) level, county/municipal level, and state level. There are approximately 6,000 police officers in Livana, all organized under the Ministry of the Interior and the National Police Headquarter in Livonia led by the First Commissioner.
Foreign Relations
Livana only recently joined the global organization, the World Forum, in 2021. Previously, the Conservative and Liberal governments maintains a persistent neutrality policy as their main foreign policy guide, and so did the People's Coalition first 5 years in power. The victory of the Coalition in 2020 brought Vera Staunton into the government, who pushed aggressively for a more active international role, and helped bolster support within the College of Representative, resulting in the ratification of the World Forum’s Charter and Livana's entrance as a full member.
Livana is a founding member of the Cross Mediterranean Economic Community (CMEC), an organization aiming to establish a single market in the Mediterranean region. Through this organization, the Livanan economy has been integrated into the greater regional economy. Livana has a close bilateral relationship with Sallodesia; in 2022, the government approved a Sallodesian military base in its territory which created controversies amongst the government and incurred protests from the Liberals and Conservatives.
Military
Main Article: Livanan Armed Forces

The Livanan Armed Forces (Militum Livana) are the military and paramilitary forces of Livana, under the President of the Confederacy as supreme commander. They consist of the Army, Navy, the Air Force, and the Marines. Overall, there is around 80,000 military personnel in Livana. Most high-ranked personnel are trained in the Simone Military Academy in Canna, although the bulk of the professional personnel of Livana came from lower academic background.
Annual conscription on a region-to-region basis (rotating between cities and counties across the three republics) is mandatory for 17 to 30 years old male citizens. There are also numerous women volunteer organizations managed by the army, allowing female citizens to participate in training and joins the reservist pool. Many paramilitary, martial art and self-defense group exist and are chartered by the Ministry of Defense. Members of these organizations are not obliged to follow conscription training because they're already trained full time and are considered part of the military, ready to be mobilized in times of need.
Administrative Divisions
Main Article: Livanan Administrative Division
Livana is a confederation of three states; Northern Liv, Southern Liv, and Cinis. Each state is led by a governor and has its own legislative body. State governments preside over regional issues such as civil defense, emergency response, as well as education and healthcare facilities. The state is then further divided into municipalities/cities (urban areas) and counties (rural areas), led by a Mayor and Regent respectively. This second-level division has greater powers over local infrastructure, as well as local security and communal services such as cultural events and charities. Municipalities are divided into wards, while counties are divided into districts. Both wards and districts are led by Supervisors and are responsible to allocate the distribution of electricity, gas, water, and internet services, as well as civil administration, acting as the first level of bureaucracy in the government.
Economy
Main Article: Economy of Livana

The Livanan economy went through a significant recovery since Livana’s second bankruptcy in 1979, with growth averaging 9.1% between 1990 and 2010. Since 2011 the growth has been pretty stagnant, averaging only around 4,2% annually.
Livana has a very high level of public debt and large external financing needs. The 2010 public debt exceeded 89.7% of GDP, one of the highest in the world as a percentage of GDP, though down from 154.8% in 1990. At the end of 1983, finance minister Alfred Robb stated that the debt was going to reach $47 billion in that year and would increase to $49 billion if the government didn’t continue its privatization effort following the Tarsis Regime. However, since then, the public debt has been managed conscientiously, and the government now turns its focus to reducing foreign debts, especially amidst rising geopolitical tension in Pacifica.
The urban population in Livana is noted for its commercial enterprise. Livana has one of the highest rates of skilled workforce in its population. This has led to an active investment market in Livana proper. The Investment Development Authority of Livana was established with the aim of promoting investment in the nation. In 2001, the Edict of Investment Regulation is passed by the Parliament to strengthen the organization's role in managing investment in Livana.

The agricultural sector employs 22% of the total workforce. Agriculture contributed to 24% of the country's GDP in 2020. Livana's major agricultural produce includes grapes (and wine), olives, barley, and lemons. The commodities market in Livana includes substantial coal production, centered on Cinis. Oil has recently been discovered offshore east of the country, and in the seabed between Southern Liv and Cinis. Talks are underway between the states to reach an agreement regarding the exploration of these resources. The seabed surrounding Livana is believed to hold significant quantities of crude oil and natural gas. Industry in Livana is mainly limited to first-level manufacturing and commodity refinement. In 2020, manufacturing ranked first as an employment source, with 36% of the Livanan working population, and first in GDP contribution, with 42% of Livana's GDP.
Nearly 28% of the Livanan workforce attain employment in the services sector. The GDP contribution of this sector amounts to roughly 34% of the annual Livanan GDP. Main service employments are in the tourism and banking sectors. The rest of the Livanan workforce are self-employed in household industries. Livana has a very low unemployment figure compared to other Pacifica nations.
Industry and Manufacturing
Southern Liv is Livana's manufacturing heartland. Large number of industrial installations are concentrated in the periphery of Greater Livonia (Livonia's urban metro area) due to the availability of a cheaper, well-educated labor workforce and proximity with the country's highways. The most prominent industries are steel production and coal refinery. Steel production accounted for 22% of Livana's manufacture and employed around 450,000 people.
The biggest amongst steel manufacturing companies is the state-owned Livanan Steel Corporation which holds 32% of Livana's steel market. The corporation has been established during the Tarsis Regime and was entirely controlled by the state, before being partially privatized after the 1979 bankruptcy. Some production lines centered around steel do exist, mainly in appliance production. However, most steels produced in Livana are exported.

In Southern Liv, there are 12 manufacturing centers for daily appliances, collectively employing around 60,000 people. Most of these installations are owned by Terrence and Bentham Industries which is privately owned by the Bentham Family and since 2010, has dominated Livana's appliance market, with a 70% market share. The company has been in close cooperation with Livanan Steel Corporation. In 2010, the government bought 20% of the company's share and managed to lower appliance prices with subsidies which eventually led Terrence and Bentham Industries to dominate the market.
Coal refining is the second biggest employer in Livana's industry, employing between 350,000 to 400,000. The industry is mainly centered in Cinis, due to its abundance of coal mines. Most coals are refined on the island and are shipped to Livonia before being exported. The biggest coal refinery company is Gunther Refinement, which accounted for almost 30% of refined coal production in Livana. Most coals mined in Livana are refined to increase their price when they are exported. Steel manufacturing and state-owned coal power plant is the biggest buyer of coal domestically.
Agriculture and Mining

Northern Liv holds almost 60% of Livana's farmlands and is considered to be Livana's agricultural center. Livana's largest agricultural product is wine, which accounted for around 15% of the country's total agricultural output. Livanan vineyards and wine production are fairly decentralized, with the biggest vineyard and wine producer in the nation, Gavarfa Vineyard, only holding 7% of the domestic market, and 12% of Livana's wine export. Most of the vineyards are concentrated near coastal areas in Northern and Southern Liv. Wine production is followed by wheat production (13% of total output), and dairy production (10% of total output). Most wheat consumed in Livana is imported, due to Livana's small territory which limits the production of wheat. Dairy products such as cheese and yogurt are exported in large numbers and are dominated by Huffer Dairies which accounted for about 40% of Livana's domestic dairy market and 60% of dairy exports. Cattle growing are still the biggest market for domestic wheat producers.
Mining and prospecting are some of the most considerable employers in Livana. The biggest mining corporation in Livana, the state-owned Livanan Mining Corporation employs almost 100,000 people, mostly from Cinis. The company diversified its mining and prospecting activities to various kinds of ores but is dominated mainly by iron ore and coal mining. Some branches of the company also mined for precious ores and minerals. The Livanan Mining Corporation holds 40% share of domestic market, and only 2% of ore export. Private companies mining in Livana are mostly foreign owned, and/or export oriented. Marble mining is advent in Aften Island, and are dominated by Kuril Marbles which owned almost a quarter of the island. Unsustainable mining activities in Livana has seen criticism in the last few years, and some parts of the government and the legislation are pushing edicts for a more sustainable approach in resource management.
Tourism

Livana is a well known tourist destination in Pacifica. Tourism contributed almost 13% of Livana's GDP, and employs around 450,000 people. Livanan coast is world renowned due to its Mediterranean climate. 60% of tourists visit Livana for activities inside Livana's coastal areas. Many resorts and hotels opened after the end of the Tarsis Regime, but the most historic hotels have been around since before the republic. The most luxurious of these hotels can be found close to the coastal area. Beaches such as Vannery Beach, offer waterfront resorts, yachting facilities, and surfing. Surfing and water sports are considered best on Livana's eastern coasts, while the western coast offers smaller waves and a better place for snorkeling.
Cultural tourism is second to coastal tourism in terms of the number of tourists. Most cultural tourism involves visitations to historic areas around Livana, and countryside experiences. Vineyards are open for tours and some prominent ones offer lodgings and wine tasting events. The government encourage locals to open guesthouses and will subsidize local tourism effort.
Domestic and foreign tourists have access to discount cards for transportation and visits to government-owned tourist attractions. Private to-rent yachts and public ferry services are available to visit Cinis and Aften Island.
Livanan Riviera

Main Article: Livanan Riviera The Livanan Riviera is a group of sheltered ports inside Riviera Bay, mainly serving yachts and cruise liners. The coast is renowned for its beachside promenade, exclusive villas near the shorelines, five-star hotels, and high-end boutiques. The ports are administrated by the Livanan Marina Guild, a council of representatives dating back to 1851 consisted out of various leisure corporations that have opened in the area, as well as representatives from the local government (Calver Municipality, Revel County, and Marina County).
Since the 90s, the area has seen a massive increase in tourists, resulting in the special economic grant given by the government to the Guild in 1991. The Riviera is serviced by the Livonia International Airport 20 km to the south, with a direct commuter line to and from the airport. In 2019, around 1.5 million visits are noted in the area. The Bay is a prime spot for foreign tourists to enjoy the Mediterranean sea. Most visitors are southerners from colder climates. By 2020, the Riviera is one of the most visited attractions in Pacifica, and has attracted foreign investments through the CMEC; in 2022, Myrian Corporation, Tannos Luxury Yacht, invested heavily in luxury yacht dockyards to accommodate more yachting activities in the marina and attracts higher-income tourists.
Infrastructure
Education

Education in Livana is free and mandatory from ages six to sixteen, and consists of four stages: primary school (primaria schola), junior high school (iunior princeps schola), senior high school (maior princeps schola) and university (universitates). All Livanan schools are required to follow a prescribed curriculum designed by the Ministry of Education. Some of the 1,400 private schools offer international programs, and may also add more courses to their curriculum with approval from the Ministry of Education.
Livana has forty-five nationally accredited universities, 16 of which are state-run universities, several of which are internationally recognized. The Livonian State University and the Calmin Social Institute were some of the most respected higher-learning institutions in the nation. Universities in Livana, both public and private, largely operate using Austral as lingua franca.
Some of the top-ranking universities in the country are the Livonia State University, Canna Technological Institute, Calmin Social Institute, Varana Pyrothecnic, and Milver School of Economics.
Health

In 2020, spending on healthcare accounted for 9.93% of the country's GDP. In 2009, there were 31.29 physicians and 19.71 nurses per 10,000 inhabitants. The life expectancy at birth was 79.59 years in 2015, or 78.48 years for males and 81.80 years for females.
By the end of the civil war, only one-third of the country's public hospitals were operational, each with an average of 20 beds. By 2009 the country had 68 public hospitals, with a total of 2,550 beds. At public hospitals, hospitalized uninsured patients pay 5% of the bill, in comparison with 15% in private hospitals, with the Ministry of Public Health reimbursing the remainder. The Ministry of Health and Welfare also has contracts with 138 private hospitals.
In 2010, there were 236,643 subsidized admissions to hospitals; 164,244 in private hospitals, and 72,399 in public hospitals. More patients visit private hospitals than public hospitals because the private bed supply is higher. To accommodate this, in 2019, the government launched a medical care-for-all program through a public-funded insurance program. This has significantly increased public hospital usage and also pushed for an increase in health spending by the government.
Demographics
The population of Livana was estimated to be 6,856,721 in 2021, with the number of Livanan nationals estimated to be 6,842,052 (July 2021 est.). Livana has a bigger percentage of women than men, with the total number of women in Livana reaching 3,584,900 while the number of men reaching 3,257,152 (more than 200,000 in difference).
The fertility rate fell from 5.00 in 1971 to 1.75 in 2004. Most Livanan are still younger than 40 years old, with the largest group belonging to the age range of 0-20 years. With the averagely good living condition, there are more than 100,000 Livanan aged more than 85 years.
Largest Cities in Livana
Religion
Main Article: Cultus Rationem

The Cultus Rationem is the largest religious group in Livana, being adhered to by more than 90% of the populace according to the 2020 census. Ordinary Livanan did not identify themselves as excessively religious, with a huge percentage of Cultus Rationem adherents (32,5%) identifying as agnostics, predominantly amongst the younger generation. Other beliefs existed, mainly brought from aboard, while 3,87% of the populace refused religious specification in their census forms. Religious holy days, especially the Day of Saints are celebrated as a national holiday, and the government took an active role in participating and promoting it. Through the Court of Morality, the theocracy holds a huge influence on Livana’s legal bureaucracy. Most judges have at least a few years of education in religious school, while three out of the seven Supreme Court Judges are former Priests/Priestesses. There is no deliberate passage on the separation of church and state in the Livanan constitution, although in general, people treated the theocracy as a social organization rather than an influential power broker.
Language
Main Article: Livanan Language
The Livanan language is part of the Tolosance family language originating in the now modern nation of Stoinia, within the category of Eastern Tolosance. It shares similar structure and syntax with several Tolosance communities in Eastern Bailtem, especially with Eria, and several extinct Tolosance communities within Pelinai. The language has drifted far enough from its Tolosance roots that it is non mutually intelligible with other Tolosance languages such as Stoinian Tarnese. Livanan received enormous Austral influence in the medieval and early modern period, mainly through the influence of seafaring merchants.
Culture
Livanan culture revolves around its historical heritage and traditional Mediterranean culture. Through trade and interactions with the rest of the world, granted by its strategic geographic position, Livana garnered an almost cosmopolitan mixture of cultures into its national identity. Successive invaders, as well as the tremendous influence of Austral on Livanan society also contributed to the robustness and uniqueness of Livana’s cultural identity.
Arts and Architecture

Modern Livanan society has various artistic lines, and many artists formed local artistic movements and held exhibitions annually. The largest artistic movement in Livana revolves around naturalism and realism. Mount Carna and Aften Island have been great sites for naturalist painters and artists, while Livana's history, mainly during the renaissance, is highly depicted in realist lines. The National Museum for Art in Livonia is the biggest curator for painting and sculpture in Livana. The museum has a joint partnership with the Livanan Art Institute and many local exhibitions. The Museum also held an annual scholarship competition for high school and college students in the form of fine and applied arts.
Rendon Martin was considered as one of the greatest naturalist painter in Livana. In his active years between 1870 to 1910, he made an estimated 5,000 unique paintings of Livana’s natural beauty, landscapes, as well as cityscapes and portraits. His favorite painting, the Red Mountain, was bought by the Livanan National Art Gallery for ₣40 million in 2015. His name was consecrated as the name of the mountain he drew in that painting, Mount Rendon.

Excellent classical arts dating back to the Tolosan civilization still survived and preserved in Livana, protected by the government as historical heritage of great importance. Sites such as Hiron are protected from development, placed inside a National Park, or moved into museums if viable. Neo-classical architectures especially built around the Livanan Renaissance are also protected from demolition and are subsidised to maintain their upkeep. Throughout the renaissance, classical Tolosan architecture were revived, and would transform into Livanan baroque which defined many historical buildings, especially related to the royalty and the nobility. These buildings suffered vandalism during the Years of Insurrection, but eventually was restored and, for most of them, came under government custody.
Literature

Livanan literature developed firmly through the Livanan Renaissance, and then through the Republican era. Famous Livanan writers are mainly tragic and fiction writers, with novel publishing, reaching its peak in the 19th century. One of the most famous writers in Livana's history is Jean Gilucca who was active throughout the 30s. His most acclaimed writings are the novel The Shining Altar and A Maiden from Cinis which focused on the lives and struggles of poor Livanan, questioning equity and fairness in Livana's civilization. Poetry is taught in schools as part of the curriculum and can be pursued in many universities in Livana. Meredith Cumberbatch was considered to be the best poet in Livana’s history. Her poems focused on the great struggle for democracy during the Tarsis era, as well as her own personal experiences through the harshness of the 50s and 60s. She was granted the National Poet Laureate in 1983 by Jeremy Clinton.
Music

Music has been an integral part of Livana's culture. While traditional folk music remains popular in Livana, modern music reconciling Austral and traditional styles, pop, and fusion are rapidly advancing in popularity. Livanan artists from the 19th century, such as the composers Ferrel Mathius, Marvin Ecklehart, and Humphrey Lyra are widely known and appreciated across Pacifica, bringing Livana's influence to the creation of modern opera and classical music.
Today, radio stations feature a variety of music, including traditional Livanan musics, classical genre, and modern Austral pop music. Livana held the annual Solstice Festival in major cities, held on June 15th to 22nd. The festival includes school marching band competitions, musical parades, country and folk song concerts, and ends with a classical concert with a firework display. Alongside the festivity, the government subsidised venues for craftsmen and ordinary folks to sell instruments and offer learning courses.
Media and Cinema

The cinema of Livana has been in existence since the 1920s, and the country has produced over 500 films with many films including Livanan filmmakers and film stars. One of the most respected and highly praised movie produced in Livana was the 1939 movie A Night with Mr. John starring John 'Steward' Varnius and young Ashley Corelia. Livana has been a popular filming site for decades due to its natural beauty and picturesque countryside. This has led to the Ministry of Tourism and Creative Economy to launch a subsidy program to help foreign studios to film their movies in Livana, and also to help bolsters small Livanan content creators.
The media of Livana is not only a regional center of production but one of the freest in Pacifica. Despite its small population and geographic size, Livana plays an influential role in the production of information in the Mediterranean and is at the core of a regional media network with global implications. The state-owned media of Livana, Nuntium Propelante, has been known to criticize the government even though 75% of its funding came from the government.
Holidays and Festivals

There are 4 national holidays in Livana. These are :
- Union Day (September 26th)
- Freedom Day (June 17th)
- Day of Saints (December 25th)
- New Year (January 1st)
- Foramil Day (March 4th)
International holidays, such as International Women’s Day, International Labour Day, Earth Day, etc. are also celebrated, although the government only recognized International Women’s Day and International Labour Day as official holidays. Apart from the 5 national holidays and the numerous international holidays, each state and locality have its own additional special days, such as Carna Day (February 12th) in Northern Liv, the Sanctuary Day (4th of June) in Aften, and City Day (September 1st) in Livonia.
Cuisine

The Livanan cuisine has developed through centuries of social and political changes, with roots as far back as the 11th century BC. Significant changes occurred during the Livanan Renaissance with the introduction of items such as potatoes, tomatoes, bell peppers and maize, now central to the cuisine but not introduced in quantity until the 18th century. Livanan cuisine is noted for its regional diversity, abundance of difference in taste. The category Livanan national dish promoted by the Government includes ied oryza, essentially a seafood fried rice with various local recipes and additional ingredients, caro crustum, a meat pie made from finely minced lamb, and sem, a salad made from parsley, tomatoes, and olives eaten with fried bread. Livanan restaurant meals begin with a wide array of spelta - small savoury breads and filled fried pastries. The spelta are typically followed by a selection of grilled meat or cheese. In general, meals are finished with wine or coffee and fresh fruits, though sometimes a selection of traditional sweets will be offered as well.

Livanan households held weekly Festum Dinner on which great courses are served, centered on fish-based dishes. Apart from Festum, daily Livanan cuisine revolves around seafood and Mediterranean produce. Olive oil and grapes are extensively used in dishes, especially in Liv. Wine is cheaper in Livana, but is only drunk during festivities and long holidays. Dairy products such as milk and cheese are very popular, especially with the older generation. Most dairy products are imported, with exceptions that are locally produced, such as the Carnian Cheese which is a local product of Northern Liv and its trade is protected by Livanan law. Most essential food supplies in Livana are imported, especially grains and cereals due to Livana's limited landmass unable to support its dense population. This has increased the popularity of foreign cuisines that enter Livanan market, especially from Myria which comprised the largest share of imported grain in Livana compared to other countries.
Sport

Football is the most popular sport in Livana. Most schools in the country sport at least one football field. Localities at the district and state levels usually have their own local football club, representing their district in state, or national level competitions. The largest football competition in Livana is the Presidential League which ran through summer. The league involves the winner of state-level eliminations. Cannan Rubrum is the dominating football team of Livana, with the most wins in the league in the past two decades (8 out of 20). Hamish Redhorn is one of the most known football athletes in Livana and he played for Cannan Rubrum before his retirement in 2015.

Apart from football, basketball and badminton are pretty popular. Most people can play badminton and badminton competitions are also held side by side with football competitions. The Foramil Badminton Cup is held in the autumn, seen as the highest national badminton competition. Rugby league is a relatively new but growing sport in Livana. Livonia and Varana hold an annual senior high school rugby league since 2010, introducing rugby into the education world.
Water sports have always been a huge part of Livanan life. Since the 1800s, kayaking and rowing competition has been held in various localities in Livana. In Falver, an annual windsurfing competition has been held since the 1980s and has become a huge attraction for tourists in the Marina. Children, since the age of 4, have been taught swimming and diving in pre-school, or individually by their parents.